Learning how to copy from CMD can significantly improve your efficiency when working with the Windows Command Prompt. For many users, especially those managing system files, troubleshooting errors, or performing administrative tasks, the Command Prompt is an essential tool. However, unlike graphical interfaces, it doesn’t allow standard copy-paste shortcuts by default, which often confuses beginners. Understanding the correct methods to copy text or data from the Command Prompt ensures smoother workflows and greater control over command-line operations. Once you master this simple technique, you’ll find it much easier to manage outputs, share results, and document your command history for future reference.
Understanding the Command Prompt Environment
The Command Prompt, commonly referred to as CMD, is a text-based interface that allows users to execute commands directly to the Windows operating system. It’s a powerful environment where you can control nearly every function of your computer from managing files and folders to running scripts or diagnostic tools. Despite being fundamental to system administration, CMD operates differently from standard Windows applications. For example, it doesn’t respond to familiar shortcuts like Ctrl + C or Ctrl + V for copying and pasting text unless properly configured. This design difference often leads to confusion for new users who expect the same functionality as other applications.
CMD uses a monochrome text interface that displays command inputs and outputs line by line. When executing commands that generate long lists of data or results, copying them manually becomes challenging. Knowing the correct approach to copying text from CMD helps prevent data loss, allows accurate troubleshooting, and improves your overall efficiency. Whether you are a developer, IT professional, or a curious learner, mastering this skill is a valuable step in using Windows more effectively.
Preparing CMD for Copying Text
Before you can successfully copy text from CMD, it’s important to make sure your Command Prompt is configured correctly. Different versions of Windows have slight variations in how CMD handles text selection and copying, but the general approach remains similar across versions.
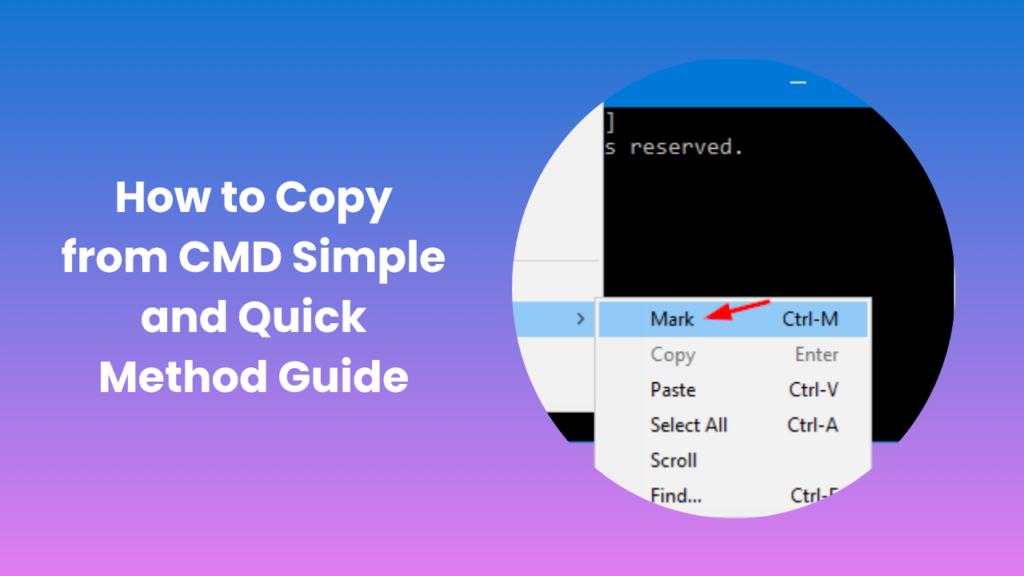
The first step in learning how to copy from CMD is to open the Command Prompt with the correct permissions. If you’re performing administrative actions, right-click the CMD icon and select “Run as administrator.” This ensures that you have full access to the commands and directories needed. Once CMD is open, you’ll notice that text selection is not immediately active; it must be manually enabled. You can do this by right-clicking the Command Prompt title bar, selecting “Properties,” and then enabling QuickEdit Mode under the “Options” tab.
Enabling QuickEdit Mode simplifies text copying within CMD. It allows you to highlight text directly with your mouse and copy it using the Enter key or by right-clicking. This configuration essentially makes CMD behave more like a traditional text interface. Once you’ve set it up, you can easily highlight any command output, press Enter to copy it, and paste it into a text editor or document. This configuration only needs to be done once, as CMD will remember your preferences for future sessions.
Step-by-Step Process for Copying Text
Once QuickEdit Mode is enabled, copying text becomes intuitive. You simply click and drag your mouse over the portion of text you wish to copy. When you release the mouse button, press Enter, and the highlighted text is automatically copied to your clipboard. You can then paste it anywhere you like into a document, email, or text editor — using Ctrl + V.
If QuickEdit Mode isn’t enabled, the process requires a few more steps. You’ll need to right-click anywhere inside the CMD window, select Mark, then drag your mouse over the text you want to copy. Press Enter to complete the process. Though slightly more manual, this method works reliably on all Windows versions.
For users working with large outputs, such as log files or directory listings, copying all text can be cumbersome. In such cases, you can redirect the command’s output to a text file using a simple syntax like command > filename.txt. This saves the entire command output into a file, which can then be opened and copied easily from any text editor. While this isn’t technically copying from CMD’s screen, it achieves the same result in a more manageable way.
Common Mistakes When Copying from Command Prompt
Many users make small but frustrating errors when trying to copy from the Command Prompt for the first time. The most common mistake is assuming that Ctrl + C will copy text as it does in other applications. In CMD, Ctrl + C actually interrupts the running command instead of copying the text, which can lead to loss of progress if a process is ongoing.
Another frequent issue arises from failing to enable QuickEdit Mode. Without it, text selection is disabled, and users often get stuck trying to highlight text using their keyboard or mouse without success. Additionally, users may not realize that CMD uses a fixed-width font and a non-wrapping display, meaning copied text may include unwanted spaces or line breaks if not selected carefully.
Understanding these nuances helps avoid frustration and ensures smoother command-line operations. Once you’ve practiced the correct method, copying and pasting from CMD becomes second nature.
Advanced Copying Options for Power Users
For advanced users or those who work frequently with CMD, there are several alternative methods to copy large volumes of text efficiently. One powerful option is using PowerShell, which provides enhanced clipboard control and supports commands like Get-Content and Set-Clipboard for automated text handling.
Another efficient method is using output redirection, which allows users to save command results directly to a text file. This can be done by adding > output.txt to the end of a command, saving the command output directly into a file in the same directory. You can later open that file with any text editor, select all, and copy it for sharing or recordkeeping.
Some users also prefer using the Windows Terminal, a modern command-line interface that integrates CMD, PowerShell, and WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) in one unified environment. The Windows Terminal supports native keyboard shortcuts for copy and paste, such as Ctrl + Shift + C and Ctrl + Shift + V, making the process faster and more intuitive.
These advanced options can drastically improve your workflow if you work regularly with command-line tools, scripts, or system diagnostics.
Troubleshooting Copy Issues
Sometimes, copying from CMD doesn’t work as expected, even when QuickEdit Mode is enabled. One reason could be a corrupted configuration or outdated system files. In such cases, resetting CMD properties or running the Command Prompt as an administrator may fix the issue.
If you find that highlighting text doesn’t copy correctly, double-check whether QuickEdit Mode is still active. Occasionally, certain Windows updates or permissions may disable it temporarily. Another potential cause is interference from third-party software that manages your clipboard. Try disabling such software temporarily and see if the problem resolves.
For users running automated scripts or working on network systems, copying text might also be limited by permission settings. Always ensure that your user account has the proper privileges to access and copy the necessary data.
FAQs
Why can’t I use Ctrl + C to copy text in CMD?
Ctrl + C doesn’t copy text; it stops running commands. Enable QuickEdit Mode or use the right-click “Mark” option to copy properly.
How can I paste text into CMD?
After enabling QuickEdit Mode, simply right-click inside CMD or use Ctrl + Shift + V in Windows Terminal to paste commands easily.
Does copying from CMD include hidden characters?
No, CMD doesn’t include hidden characters, but sometimes extra spaces or line breaks may appear due to the text format.
Can I copy CMD output automatically?
Yes, use > output.txt after a command to save its output to a text file, which you can open and copy anytime.
What’s the difference between CMD and PowerShell for copying text?
PowerShell supports built-in clipboard commands, while CMD requires manual copying using QuickEdit Mode or marking text.
How do I copy the full screen output of CMD?
Right-click the CMD title bar, select Edit → Select All, and press Enter to copy the entire visible content.
Why does my copied text from CMD include extra spaces or breaks?
This happens when lines wrap automatically. Adjust the CMD window width before copying to reduce spacing issues.
Conclusion
Knowing how to copy from CMD is a small but powerful skill that simplifies your interaction with the Windows Command Prompt. It allows you to document command results, share outputs, and troubleshoot systems more effectively. Once you’ve enabled QuickEdit Mode and understood the correct methods, copying text becomes an effortless part of your workflow. This not only enhances your productivity but also helps maintain a clear record of your work. Whether you’re a beginner exploring CMD for the first time or a professional managing complex systems, mastering this process is a valuable step toward becoming more efficient and confident in using Windows command-line tools.